Jewel Cave National Monument on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Jewel Cave National Monument contains Jewel Cave, currently the third longest cave in the world, with of mapped passageways. It is located approximately west of the town of
 As recently as 1959, less than of passageway had been discovered. That year, however,
As recently as 1959, less than of passageway had been discovered. That year, however,
 By 1979,
By 1979,
 Jewel Cave is a "breathing cave," which means air enters or exits the cave with changes in
Jewel Cave is a "breathing cave," which means air enters or exits the cave with changes in
File:Jewel Cave 1.jpg, Much of Jewel Cave is covered with spar crystals, but they are rarely as clear as this cluster.
File:Jewel Cave 2.jpg, Spar crystals cover much of the walls in some sections of the cave. Typically they are a dull brown color as in this room.
File:Jewel Cave 3.jpg, Aragonite frostwork is another speleothem found throughout the cave, typically in small crusts on the walls.
File:JECA formations.jpg, Calcite crystals in Jewel Cave
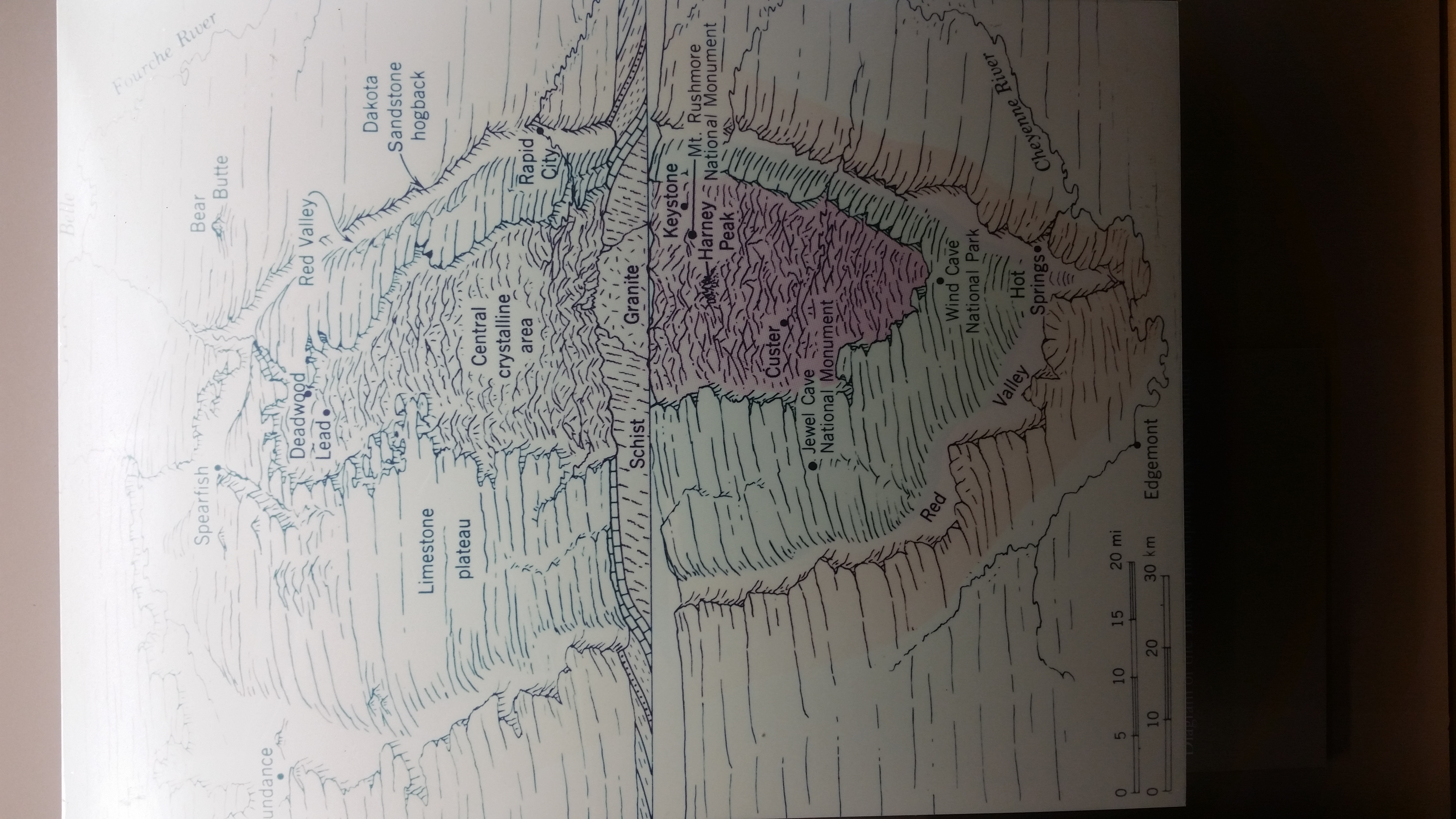
Custer
George Armstrong Custer (December 5, 1839 – June 25, 1876) was a United States Army officer and cavalry commander in the American Civil War and the American Indian Wars.
Custer graduated from West Point in 1861 at the bottom of his class, b ...
in Black Hills
The Black Hills ( lkt, Ȟe Sápa; chy, Moʼȯhta-voʼhonáaeva; hid, awaxaawi shiibisha) is an isolated mountain range rising from the Great Plains of North America in western South Dakota and extending into Wyoming, United States. Black Elk P ...
of South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota people, Lakota and Dakota peo ...
. It became a national monument
A national monument is a monument constructed in order to commemorate something of importance to national heritage, such as a country's founding, independence, war, or the life and death of a historical figure.
The term may also refer to a spec ...
in 1908.
History
Frank and Albert Michaud, two local prospectors, discovered the cave in 1900, when they felt cold air blowing out of a small hole in a canyon. It is unknown whether any previous inhabitants of the area were aware of the natural cave opening, which was not large enough for a person to enter.Jewel Cave brochure; National Park Service; GPO, WDC After enlarging the cave entrance with dynamite, the Michaud brothers found a cavern lined withcalcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
crystals, which led them to name it "Jewel Cave". The brothers tried to capitalize on the discovery, widening the opening, building walkways inside, and opening it to tourists. Although their venture was unsuccessful, news of the discovery eventually reached Washington. President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
proclaimed Jewel Cave a National Monument on February 7, 1908. The area around the natural entrance to the cave was further developed by the Civilian Conservation Corps
The Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) was a voluntary government work relief program that ran from 1933 to 1942 in the United States for unemployed, unmarried men ages 18–25 and eventually expanded to ages 17–28. The CCC was a major part of ...
in the 1930s. The National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational propertie ...
assumed management of the monument in 1933 and began offering tours in 1939.
 As recently as 1959, less than of passageway had been discovered. That year, however,
As recently as 1959, less than of passageway had been discovered. That year, however, Herb and Jan Conn
Jan Conn (born 1924 ) and Herb Conn (April 16, 1920 – February 1, 2012www.findagrave.com
...
, local rock climbers, began exploring, and within two years had mapped . Much of the new discoveries lay outside the boundaries of the monument, under land managed by the ...
United States Forest Service
The United States Forest Service (USFS) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Agriculture that administers the nation's 154 national forests and 20 national grasslands. The Forest Service manages of land. Major divisions of the agency inc ...
. The two agencies performed a land swap in 1965, establishing the present boundaries of the park, and enabling the development of a new part of the cave. The Park Service sunk a elevator shaft to a previously remote cave area, and built concrete walks and metal stairs and platforms along a one-half-mile loop. The "Scenic Tour" was opened in 1972. Most modern-day visitors tour that part of the cave.
In August 2000, an forest fire
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of Combustibility and flammability, combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire ...
burned 90% of the monument and the surrounding area. The visitor center
A visitor center or centre (see American and British English spelling differences), visitor information center, tourist information center, is a physical location that provides tourist information to visitors.
Types of visitor center
A visit ...
and historic buildings were spared.
Exploration
 By 1979,
By 1979, Herb and Jan Conn
Jan Conn (born 1924 ) and Herb Conn (April 16, 1920 – February 1, 2012www.findagrave.com
...
had discovered, named, and mapped more than of passages. Although they largely retired from caving by the early 1980s, exploration has continued unabated. Because the areas being explored take many hours to reach, explorers now sometimes camp in the cave during expeditions of as long as four days. The cave is mapped by traditional survey techniques, using ...
compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with ...
, clinometer
An inclinometer or clinometer is an instrument used for measuring angles of slope, elevation, or depression of an object with respect to gravity's direction. It is also known as a ''tilt indicator'', ''tilt sensor'', ''tilt meter'', ''slope ...
and today with lasers instead of tape measures.
Its of mapped passageway make Jewel Cave the third longest cave in the world, after Mammoth Cave
Mammoth Cave National Park is an American national park in west-central Kentucky, encompassing portions of Mammoth Cave, the longest cave system known in the world.
Since the 1972 unification of Mammoth Cave with the even-longer system under F ...
System in Kentucky and Sistema Sac Actun
Sistema Sac Actun (from Spanish and Yucatec Maya meaning "White Cave System") is an underwater cave system situated along the Caribbean coast of the Yucatán Peninsula with passages to the north and west of the city of Tulum. Discovery of a connec ...
at the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
(Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
).
The discovered areas in the cave account for only about 3 to 5% of the estimated total air volume of the cave. The cave volume is estimated by measuring the amount of air that the cave "exhales" when the outside air pressure drops and "inhales" when the outside air pressure rises.
Geology
 Jewel Cave is a "breathing cave," which means air enters or exits the cave with changes in
Jewel Cave is a "breathing cave," which means air enters or exits the cave with changes in atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 7 ...
from day to night or due to changes in the weather. This was first explained by Herb Conn in 1966.
Most of the cave formed within the Mississippian Pahasapa Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
deposited 350 million years ago. The later limestones, sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) ...
s, and shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
s deposited in these Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
and Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceo ...
seas were eroded with the geologic uplift
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted ...
associated with Laramide Orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the o ...
and the formation of the Black Hills
The Black Hills ( lkt, Ȟe Sápa; chy, Moʼȯhta-voʼhonáaeva; hid, awaxaawi shiibisha) is an isolated mountain range rising from the Great Plains of North America in western South Dakota and extending into Wyoming, United States. Black Elk P ...
. The main passages of the cave then formed in the early Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
. Uplift continued in the Late Pliocene
Late may refer to:
* LATE, an acronym which could stand for:
** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia
** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law
** Local average treatment effect, ...
or Early Pleistocene
The Early Pleistocene is an unofficial sub-epoch in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently estimated to span the time ...
lowering the water table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.
T ...
and draining the cave.
Jewel Cave passages follow a pattern of joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw ...
development. The faults and joints are associated with the uplift of the Black Hills approximately 58 to 54 million years ago. After main cave dissolution
Dissolution may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Books
* ''Dissolution'' (''Forgotten Realms'' novel), a 2002 fantasy novel by Richard Lee Byers
* ''Dissolution'' (Sansom novel), a 2003 historical novel by C. J. Sansom Music
* Dissolution, in mu ...
, a thick layer of calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
lined the walls about 2.5 million years ago.
During cave development and afterwards, speleothems
A speleothem (; ) is a geological formation by mineral deposition (geology), deposits that accumulate over time in natural caves. Speleothems most commonly form in calcareous caves due to carbonate dissolution reactions. They can take a variety ...
and speleogen
A speleogen is a geological feature within a karst system that is created by the dissolution of bedrock. As rain water falls through the atmosphere it picks up carbon dioxide and more as it passes through organic material in the soil. As water mov ...
s formed, including the "jewels" or spar
SPAR, originally DESPAR, styled as DE SPAR, is a Dutch multinational that provides branding, supplies and support services for independently owned and operated food retail stores. It was founded in the Netherlands in 1932, by Adriaan van Well, ...
. Other examples include stalactites, stalagmite
A stalagmite (, ; from the Greek , from , "dropping, trickling")
is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave due to the accumulation of material deposited on the floor from ceiling drippings. Stalagmites are typically ...
s, flowstone
Flowstones are sheetlike deposits of calcite or other carbonate minerals, formed where water flows down the walls or along the floors of a cave. They are typically found in "solution caves", in limestone, where they are the most common speleothe ...
, cave popcorn
Cave popcorn, or coralloids, are small nodes of calcite, aragonite or gypsum that form on surfaces in caves, especially limestone caves. They are a common type of speleothem.
Appearance
The individual nodules of cave popcorn range in size from ...
, boxworks, helictite
A helictite is a speleothem (cave-formed mineral) found in a limestone cave that changes its axis from the vertical at one or more stages during its growth. Helictites have a curving or angular form that looks as if they were grown in zero grav ...
s, scintillites, conulites, coralloids, cave pearl
A cave pearl is a small, usually spherical, speleothem (cave formation) found in limestone caves. Cave pearls are formed by a concretion of calcium salts that form concentric layers around a nucleus. Exposure to moving water polishes the surface ...
s, rimstone
Rimstone, also called gours, is a type of speleothem (cave formation) in the form of a stone dam. Rimstone is made up of calcite and other minerals that build up in cave pools. The formation created, which looks like stairs, often extends into fl ...
, rafts, rims, vents, and frostwork
In geology, frostwork is a type of speleothem (cave formation) with acicular ("needle-like") growths almost always composed of aragonite (a polymorph of calcite) or calcite replaced aragonite. It is a variety of anthodite. Frostwork can also be ...
. The gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywall. ...
formations include needles, beards, cotton, hair, flowers, and spiders. Finally, Jewel Cave contains a very rare formation called a hydromagnesite
Hydromagnesite is a hydrated magnesium carbonate mineral with the formula Mg5(CO3)4(OH)2·4H2O.
It generally occurs associated with the weathering products of magnesium containing minerals such as serpentine or brucite. It occurs as incrustations ...
balloon. Those are created when gas of an unknown source inflates a pasty substance formed by the precipitation of the magnesium carbonate hydroxide mineral.
Access
Jewel Cave is open year-round. The Park Service offers three tours: the scenic tour, a half-mile loop through a paved and lighted central portion of the cave accessible by elevator; the historic tour, a candlelight tour through the earliest-discovered part of the cave; and a wild caving tour, through an undeveloped part of the cave near the scenic loop. There are 3 surface trails varying in length and difficulty.See also
*List of caves
This is a list of caves of the world that have articles or that are properly cited. They are sorted by continent and then country. Caves which are in overseas territories on a different continent than the home country are sorted by the territory' ...
*List of longest caves in the United States
The following is a list of the longest caves in the United States per length of documented passageways. Many passageways are still being discovered; this list is based on the latest verifiable data.
See also
*List of caves
*List of longest ca ...
* List of longest caves
This list of longest caves includes caves in which the combined length of documented passageways exceeds . In some of these caves, passageways are still being discovered.
Geographical distribution
Caves are found around the world. The largest ...
* Wind Cave National Park
Wind Cave National Park is an American national park located north of the town of Hot Springs in western South Dakota. Established on January 3, 1903 by President Theodore Roosevelt, it was the sixth national park in the U.S. and the first ca ...
* Mammoth Cave National Park
Mammoth Cave National Park is an American national park in west-central Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper Sout ...
* Lehman Caves
Great Basin National Park is an American national park located in White Pine County in east-central Nevada, near the Utah border, established in 1986. The park is most commonly entered by way of Nevada State Route 488, which is connected to U. ...
* Oregon Caves National Monument
Oregon Caves National Monument and Preserve is a protected area in the northern Siskiyou Mountains of southwestern Oregon in the United States. The 4,554-acre (1,843 ha) park, including the marble cave, is 20 miles (32 km) east of C ...
* Russell Cave National Monument
Russell Cave National Monument is a U.S. National Monument in northeastern Alabama, United States, close to the town of Bridgeport, Alabama, Bridgeport. The monument was established on May 11, 1961, when 310 acres (1.3 km2) of land were ...
* Timpanogos Cave National Monument
Timpanogos Cave National Monument is a United States National Monument protecting the Timpanogos Cave Historic District and a
cave system on Mount Timpanogos in American Fork Canyon in the Wasatch Range, near Highland, Utah, in the United States. ...
* Speleology
Speleology is the scientific study of caves and other karst features, as well as their make-up, structure, physical properties, history, life forms, and the processes by which they form ( speleogenesis) and change over time (speleomorphology) ...
References
* (describes the exploration of Jewel Cave from its discovery to the mid-1980s) * * {{authority control Black Hills Caves of South Dakota Show caves in the United States Protected areas of Custer County, South Dakota National Park Service National Monuments in South Dakota Protected areas established in 1908 Civilian Conservation Corps in South Dakota 1908 establishments in South Dakota Landforms of Custer County, South Dakota